Tax lien investing is an attractive option for real estate investors seeking high returns and low competition. By purchasing tax lien certificates, investors can earn significant interest rates or even acquire properties at a fraction of their market value. This article will explore the essentials of tax lien investing, including understanding tax liens, the investing process, legal considerations, and profit strategies. Whether you are a seasoned investor or new to the real estate market, this guide will equip you with the knowledge needed to navigate the tax lien investing landscape successfully.
What are Tax Liens?
Tax liens are legal claims filed by government authorities against properties whose owners have failed to pay their property taxes. When property taxes remain unpaid, the local government imposes a lien on the property to secure the owed taxes. This lien gives the government the right to collect the unpaid taxes, plus any applicable interest and penalties.
The tax lien remains attached to the property until the tax debt is paid off. If the debt is not settled within a specified period, the government can sell the tax lien to investors through an auction, allowing them to recoup the owed taxes more quickly. Investors who purchase tax liens earn the right to collect the unpaid taxes, plus interest, from the property owner. If the owner fails to pay, the investor can initiate foreclosure proceedings to gain ownership of the property.
Tax lien investing involves purchasing tax lien certificates from local government auctions. When a property owner defaults on their property taxes, the government issues a tax lien certificate representing the unpaid amount. These certificates are then auctioned to investors, who pay the outstanding taxes on behalf of the property owner.
Investors benefit in two primary ways:
- Interest Income: The property owner must repay the investor the amount of the tax lien, plus interest. The interest rate can be quite high, often ranging from 5% to 36% per annum, depending on the state and local regulations.
- Property Acquisition: If the property owner fails to redeem the lien by paying the owed amount within the redemption period, the investor can foreclose on the property and potentially acquire it at a significant discount.
Successful tax lien investing requires thorough research, due diligence, and a clear understanding of the local laws governing tax lien sales and redemptions.
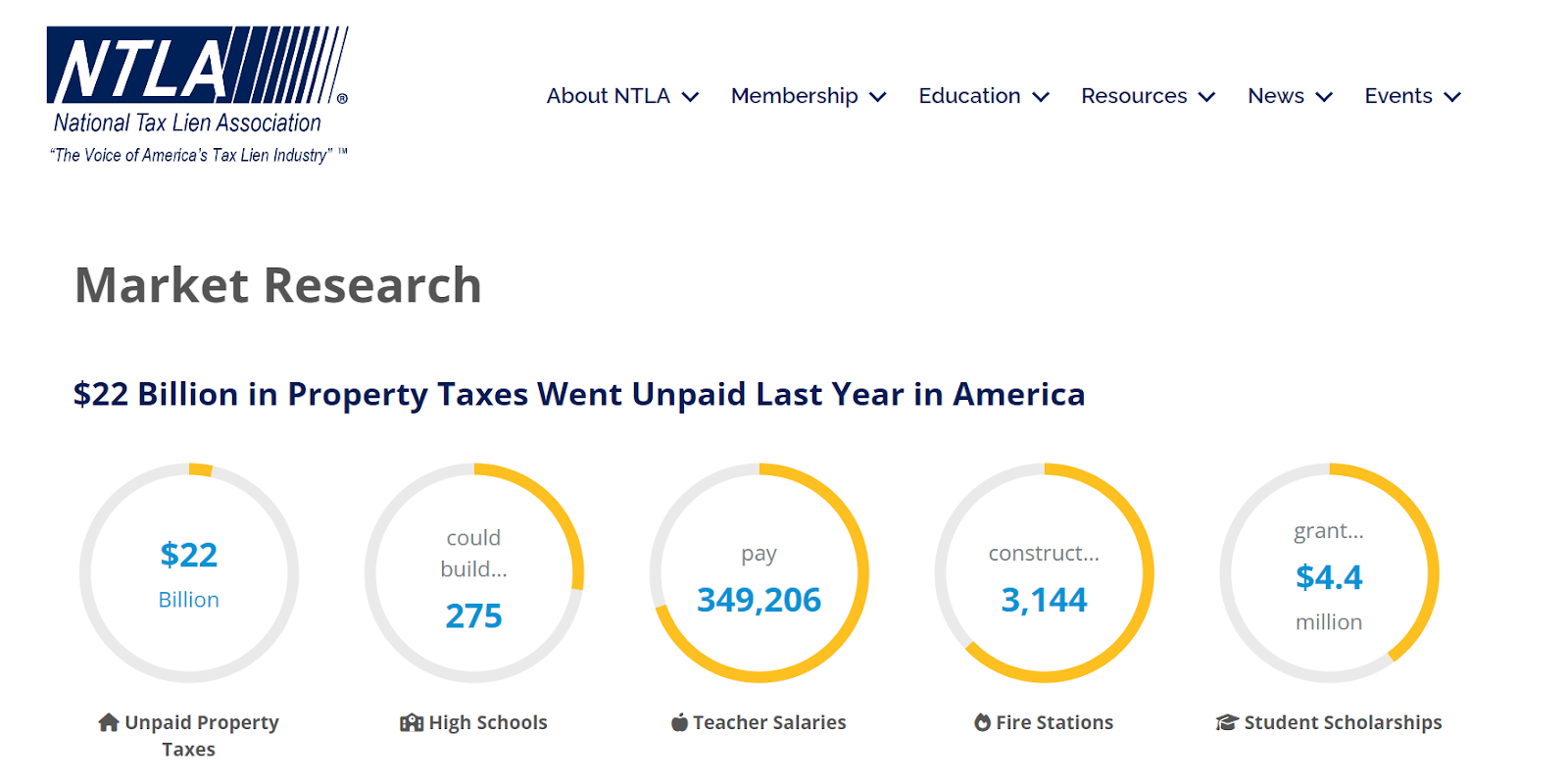
source: NTLA
Researching Tax Lien Properties
Before diving into tax lien investing, thorough research is crucial to ensure sound investment decisions. Here are the key steps involved in researching tax lien properties:
- Identify Available Properties: Local government websites often provide lists of properties with tax liens. These lists can be accessed through county tax offices or online databases dedicated to tax lien sales.
- Assess Property Value: Evaluate the market value of the properties to determine potential returns. Tools like real estate websites, county records, and appraisal reports can help gauge a property’s value and condition.
- Check Property Condition: Conduct a physical inspection, if possible, to assess the property’s condition. Properties in poor condition may require significant investment in repairs and maintenance.
- Review Tax Lien Details: Understand the specifics of the tax lien, including the amount owed, interest rates, redemption periods, and any additional fees or penalties. This information is typically available through the state or county tax office or auction platform.
- Evaluate Local Market Conditions: Consider the economic and real estate market conditions in the area where the property is located. Factors like local employment rates, population growth, and real estate trends can influence the investment’s profitability.
- Verify Legal and Zoning Issues: Ensure there are no legal disputes, zoning issues, or other encumbrances that could affect the property’s value or your ability to foreclose if necessary.
By conducting thorough research, investors can make informed decisions, minimize risks, and maximize potential returns in tax lien investing.
source: PA Lien Serach
Bidding at Tax Lien Auctions
Tax lien auctions are competitive events where investors bid on tax lien certificates. Understanding the auction process and strategies can significantly enhance your success rate. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Find Auction Information: Auctions are typically announced on county websites, newspapers, or specialized online platforms. Gather details about the auction date, location, and list of available properties.
- Register for the Auction: Many auctions require pre-registration. Ensure you complete any necessary forms and meet the financial requirements, such as providing a deposit or proof of funds.
- Understand the Bidding Process: Auctions can be conducted in various formats, including:
- Live Auctions: Held in-person at a physical location.
- Online Auctions: Conducted through internet-based platforms.
- Sealed Bid Auctions: Investors submit their bids in writing without knowing the bids of others.
- Set a Budget: Determine your maximum bid for each property based on your research. This helps avoid overbidding and ensures you maintain a profitable margin.
- Bid Strategically: During the auction, bid confidently but within your predetermined budget. Consider starting with lower bids and gradually increasing if necessary.
- Secure Your Purchase: If you win the bid, promptly pay the required amount and complete any necessary paperwork to secure the tax lien certificate.
Participating in tax lien auctions requires preparation and strategic planning. By understanding the process and being well-prepared, investors can secure profitable tax lien certificates.
Legal Considerations and Due Diligence
Engaging in tax lien investing necessitates a thorough understanding of the legal framework and diligent research to ensure compliance and mitigate risks. Here are the critical aspects to consider:
- State and Local Laws: Tax lien investing is governed by state and local regulations, which can vary significantly. Familiarize yourself with the specific laws in the state where you plan to invest. Key areas include interest rates, redemption periods, and foreclosure procedures.
- Redemption Periods: Each state sets a redemption period during which the property owner can repay the lien amount plus interest to reclaim their property. Understanding these periods is crucial, as they impact the timeline for potential returns or foreclosure actions.
- Interest Rates and Penalties: States impose varying interest rates and penalties on unpaid tax liens. Knowing these rates helps in calculating potential returns and assessing investment viability.
- Title Searches: Conduct a thorough title search to identify any other liens or encumbrances on the property. This step ensures you are aware of any existing claims that could affect your investment or lead to additional costs.
- Legal Fees and Costs: Be prepared for potential legal expenses related to enforcing the lien or initiating foreclosure proceedings. These costs should be factored into your investment calculations.
- Bankruptcy Considerations: If the property owner files for bankruptcy, the process can complicate lien enforcement. Understanding how bankruptcy affects tax liens is essential for managing such scenarios.
- Working with Professionals: Consider consulting with real estate attorneys or professionals specializing in tax lien investing. Their expertise can help navigate complex legal issues and provide valuable guidance.
Diligence in understanding and adhering to legal requirements protects investors and enhances the likelihood of successful outcomes in tax lien investing.
Acquiring and Owning Tax Lien Certificates
Acquiring tax lien certificates involves a systematic approach, from the initial purchase at auction to managing the investment until the lien is resolved. Here’s a detailed look at the process:
- Purchasing Tax Lien Certificates:
- Attend Auctions: As discussed, attend live or online auctions to purchase tax lien certificates. Ensure you have conducted thorough research and set a budget for bidding.
- Direct Purchases: In some cases, you can buy tax lien certificates directly from the county after an auction, if not all certificates are sold.
- Certificate Ownership:
- Record Keeping: Maintain accurate records of your purchased tax lien certificates, including details like the property address, lien amount, interest rate, redemption period, and any communication with the property owner or county.
- Monitoring: Regularly monitor the status of your liens. Keep track of redemption deadlines and any payments made by the property owner.
- Collecting Payments:
- Interest and Penalties: If the property owner redeems the lien, they must pay the lien amount plus any accrued interest and penalties. Ensure you receive the full payment as stipulated by the law.
- Handling Non-Payments: If the property owner fails to pay, you have the right to initiate foreclosure proceedings after the redemption period expires.
- Foreclosure Process:
- Initiate Foreclosure: If the lien is not redeemed, you can start the foreclosure process to take ownership of the property. This involves legal procedures that vary by state.
- Property Acquisition: Successfully foreclosing on the property means you gain ownership. You can then decide to sell the property, rent it out, or use it as a personal asset.
- Management and Exit Strategies:
- Property Management: If you acquire the property, consider whether you will manage it yourself or hire a property management company.
- Selling the Property: Evaluate the market conditions and potential profit from selling the property. Ensure all legal paperwork is in order before listing it for sale.
- Holding for Appreciation: You might choose to hold onto the property if the market is expected to appreciate, increasing your eventual returns.
Owning tax lien certificates can be highly profitable, but it requires meticulous management and strategic decision-making to maximize returns.
Profit Strategies in Tax Lien Investing
Maximizing profits in tax lien investing involves strategic planning and execution. Here are some key strategies to consider:
- Focus on High-Interest Rates:
- Identify High-Rate States: Invest in states with higher statutory interest rates on tax liens. States like Florida and Illinois offer rates up to 18% and 36% respectively.
- Target High-Penalty Properties: Some properties may incur additional penalties beyond the interest rate, increasing potential returns.
- Diversify Investments:
- Geographic Diversification: Spread your investments across different states and counties to minimize risk and capitalize on varying interest rates and redemption periods.
- Property Type Diversification: Invest in different types of properties, such as residential, commercial, and vacant land, to balance your portfolio and mitigate sector-specific risks.
- Participate in Secondary Market:
- Buy Existing Liens: Purchase tax liens from other investors looking to liquidate their holdings. This can provide opportunities to acquire liens at a discount.
- Sell Your Liens: If you need liquidity, consider selling your tax lien certificates on the secondary market before the redemption period ends.
- Leverage Legal Expertise:
- Hire Professionals: Engage real estate attorneys or firms specializing in tax lien investments to handle complex legal issues, foreclosures, and title clearing.
- Stay Informed: Keep abreast of changes in tax lien laws and regulations to ensure compliance and identify new opportunities.
- Foreclosure Opportunities:
- Acquire Properties: Use foreclosure as a strategy to acquire properties at a significant discount. After obtaining ownership, you can sell the property, rent it out, or hold it for appreciation.
- Improve and Sell: Invest in improving the acquired properties to increase their market value before selling, maximizing your returns.
- Use Technology:
- Online Platforms: Utilize online platforms and tools for researching, bidding, and managing tax lien investments. These platforms can streamline processes and provide valuable data.
- Data Analysis: Employ data analysis tools to identify trends, high-performing regions, and optimal investment opportunities.
- Network with Other Investors:
- Join Investor Groups: Participate in local or online investor groups to share insights, experiences, and strategies. Networking can provide access to valuable resources and opportunities.
- Attend Conferences: Real estate and investment conferences can offer education, networking, and the latest industry trends and strategies.
By implementing these profit strategies, investors can enhance their chances of achieving substantial returns from tax lien investing.
Tax Lien Redemption and Foreclosure Process
Understanding the redemption and foreclosure process is crucial for tax lien investors, as it determines whether you will earn interest or acquire the property. Here’s an in-depth look at these processes:
- Redemption Period:
- Duration: The redemption period is the time frame during which the property owner can repay the tax lien amount plus interest to reclaim their property. This period varies by state, typically ranging from a few months to several years.
- Owner Notification: During the redemption period, the property owner is often notified of the lien and the amount required to redeem it. Some states require multiple notifications to ensure the owner is aware of the lien.
- Interest Accrual: Interest on the lien amount continues to accrue throughout the redemption period, providing a steady return for the investor if the owner redeems the lien.
- Redemption Process:
- Payment: The property owner must pay the outstanding tax amount, interest, and any additional fees to the county or directly to the investor, depending on the state’s procedures.
- Receiving Payment: As the lienholder, you will receive the lien amount plus the accrued interest and penalties once the property owner redeems the lien. Ensure accurate records are maintained to verify payments and interest calculations.
- Foreclosure Initiation:
- Unredeemed Liens: If the lien is not redeemed within the redemption period, you can initiate foreclosure proceedings to gain ownership of the property.
- Legal Procedures: Foreclosure processes vary by state but generally involve filing a legal action against the property owner and obtaining a court judgment to transfer ownership. This can be a complex and time-consuming process, often requiring legal assistance.
- Acquiring the Property:
- Court Judgment: Once a court judgment is obtained, you can take possession of the property. Ensure all legal requirements are met and the title is clear of other encumbrances.
- Title Clearing: Depending on state laws, you may need to undertake additional steps to clear the title, such as addressing other liens or conducting a quiet title action to remove any claims against the property.
- Post-Foreclosure Actions:
- Property Management: After acquiring the property, decide whether to manage it yourself, hire a property management company, or sell it. Consider factors like the property’s condition, local market conditions, and your long-term investment strategy.
- Selling the Property: If you choose to sell, ensure the property is in good condition and all legal paperwork is in order. Marketing the property effectively can help achieve the best sale price.
- Rental Income: Alternatively, renting out the property can provide a steady income stream. Assess the rental market in the area and manage the property or hire a professional management firm.
The redemption and foreclosure processes are critical components of tax lien investing, impacting your overall investment strategy and potential returns. By understanding and navigating these processes effectively, investors can maximize their chances of success.
Risks and Challenges in Tax Lien Investing
While tax lien investing can be highly profitable, it also comes with inherent risks and challenges that investors must navigate carefully. Understanding these risks and preparing for potential pitfalls is crucial for success.
- Property Condition and Market Value:
- Hidden Defects: Properties associated with tax liens may have hidden structural issues or require significant repairs, which can be costly.
- Market Fluctuations: Real estate market conditions can change, affecting the property’s value and your ability to sell it at a profitable price.
- Redemption Uncertainty:
- Variable Redemption Rates: Not all property owners will redeem their liens. While some investors may welcome the opportunity to foreclose and acquire the property, others may prefer the guaranteed interest income from redemptions.
- Extended Redemption Periods: Long redemption periods can tie up your capital for years, limiting liquidity and investment flexibility.
- Foreclosure Complications:
- Legal Complexities: Foreclosure procedures vary by state and can be legally complex, time-consuming, and costly. Missteps in the process can result in delays or even loss of the investment.
- Bankruptcy Issues: If a property owner files for bankruptcy, the foreclosure process can be halted or complicated, leading to prolonged investment recovery periods.
- Competing Liens and Encumbrances:
- Senior Liens: Tax liens are usually senior to most other liens, but other encumbrances, such as mortgages, mechanic’s liens, or environmental liens, can complicate the foreclosure process and reduce the property’s value.
- Title Issues: Clearing the title after foreclosure may require additional legal steps and expenses, such as conducting a quiet title action to eliminate competing claims.
- Regulatory Changes:
- Legislative Changes: State and local governments can change tax lien laws, affecting interest rates, redemption periods, and foreclosure procedures. Staying informed about regulatory changes is essential to adjust your investment strategy accordingly.
- Policy Shifts: Policy shifts in response to economic conditions or political pressures can impact the attractiveness and viability of tax lien investing.
- Financial Risks:
- Investment Loss: There is always the risk of not recovering your investment if the property’s value is significantly lower than expected or if the property has insurmountable issues.
- Holding Costs: Costs associated with holding a property, such as maintenance, insurance, and property taxes, can add up if the property is not sold or rented out promptly after foreclosure.
- Due Diligence and Research:
- Inadequate Research: Failing to conduct thorough research on the property, local market conditions, and legal requirements can lead to poor investment decisions.
- Overbidding: Competitive bidding at auctions can sometimes lead to overbidding, reducing the potential return on investment.
By being aware of these risks and challenges and implementing strategies to mitigate them, investors can improve their chances of success in the tax lien investing arena.
Tips for Successful Tax Lien Investing
To achieve success in tax lien investing, adopting best practices and strategic approaches is essential. Here are some tips to help you navigate this investment landscape effectively:
- Educate Yourself:
- Understand the Process: Familiarize yourself with the tax lien investing process, including how tax liens are issued, auctioned, and redeemed.
- Learn State-Specific Laws: Each state has different laws governing tax lien investing. Understand the regulations, interest rates, and redemption periods in the states where you plan to invest.
- Conduct Thorough Research:
- Property Research: Investigate the properties associated with tax liens. Assess their market value, condition, and any potential issues.
- Market Analysis: Analyze the local real estate market to understand trends, demand, and economic conditions that could impact your investment.
- Diversify Your Portfolio:
- Geographic Diversification: Spread your investments across different states and counties to reduce risk and capitalize on varying interest rates and redemption periods.
- Property Type Diversification: Invest in a mix of residential, commercial, and vacant land to balance your portfolio and mitigate sector-specific risks.
- Set a Budget and Stick to It:
- Budgeting: Determine your maximum bid for each property based on your research and stick to it during auctions to avoid overbidding.
- Financial Planning: Consider all potential costs, including legal fees, property maintenance, and holding costs, in your financial planning.
- Leverage Technology and Tools:
- Online Platforms: Use online auction platforms and research tools to streamline the process and access valuable data.
- Data Analytics: Employ data analytics to identify trends, high-performing areas, and optimal investment opportunities.
- Network with Other Investors:
- Join Investor Groups: Participate in local or online investor groups to share insights, experiences, and strategies.
- Attend Conferences: Real estate and investment conferences offer education, networking, and the latest industry trends and strategies.
- Hire Professionals:
- Legal Assistance: Consult with real estate attorneys or professionals specializing in tax lien investing to handle legal issues, foreclosures, and title clearing.
- Property Management: Consider hiring a property management company if you acquire properties through foreclosure to ensure they are well-maintained and generate income.
- Monitor Your Investments:
- Record Keeping: Maintain detailed records of your tax lien certificates, including property details, lien amounts, interest rates, and redemption statuses.
- Regular Monitoring: Keep track of redemption periods and any payments made by property owners to stay informed about your investment status.
- Be Patient and Persistent:
- Long-Term Perspective: Tax lien investing can require patience, especially when waiting for redemptions or navigating foreclosure processes. Maintain a long-term perspective to achieve the best outcomes.
- Stay Informed: Continuously educate yourself about changes in tax lien laws, market conditions, and new investment opportunities.
- Evaluate and Adjust Your Strategy:
- Periodic Review: Regularly review your investment strategy and performance. Evaluate what works and what doesn’t, and adjust your approach accordingly.
- Adaptability: Be adaptable to changing market conditions, regulatory environments, and new investment opportunities to stay ahead in the tax lien investing landscape.
By following these tips, you can enhance your chances of success in tax lien investing, minimize risks, and achieve profitable returns.
FAQs
Is it too late to save my house?
It is generally not too late to save your house if a tax lien has been placed on it. Property owners typically have a redemption period during which they can pay the outstanding taxes, interest, and penalties to clear the lien. Contact your local tax office to understand the specific requirements and deadlines for redeeming your property.
How to invest in US tax liens?
To invest in US tax liens, follow these steps:
- Research: Understand state and local laws governing tax liens.
- Identify Auctions: Find tax lien auctions through county websites or online platforms.
- Register: Register for the auction and meet any financial requirements.
- Bid: Participate in the auction and place your bids on desirable properties.
- Purchase: If you win, pay for the tax lien certificate and manage your investment until the lien is redeemed or foreclosed.
What is the best state to buy tax lien certificates?
The best state to buy tax lien certificates depends on your investment goals. States like Florida and Illinois offer high interest rates (up to 18% and 36%, respectively) and well-structured auction processes. Research various states to find the best fit for your investment strategy.
How do tax liens work in Colorado?
In Colorado, tax lien certificates are sold at public auctions. Investors bid on the interest rate they are willing to accept, starting at 9% and decreasing with each bid. The property owner has three years to redeem the lien by paying the back taxes, interest, and penalties. If the lien is not redeemed within this period, the investor can initiate foreclosure proceedings to acquire the property.
How do tax liens work in Texas?
Texas tax lien investing is unique because it uses a hybrid system of tax liens and tax deeds. Investors purchase tax lien certificates at public auctions, earning a 25% penalty on the lien amount if the owner redeems within six months, or 50% if redeemed after six months but within two years. If the property is not redeemed within two years, the investor can acquire the property through foreclosure.
Wrap Up
Tax lien investing offers real estate investors high returns and the potential to acquire properties at a discount. By understanding the process, conducting thorough research, and following best practices, investors can navigate the complexities and succeed in this lucrative investment strategy. With careful planning and diligence, tax lien investing can become a profitable addition to any real estate portfolio.
